Low angle normal faults with regional tectonic significance may be designated detachment faults.
Hanging wall is downthrown in a normal fault.
Moreover the fault surface between footwall and hanging wall dips steeply.
The only difference between the normal fault and reverse fault is that in normal fault the hanging wall is downward with respect to the footwall whereas in a reverse fault the apparent movement of the hanging wall is upwards with.
Moving wall is called the hanging wall.
When a fault slips the hanging wall moves up and the footwall moves down a.
Such faults are typically regional in nature and develop as a response to extensional collapse of a passive continental margin i e.
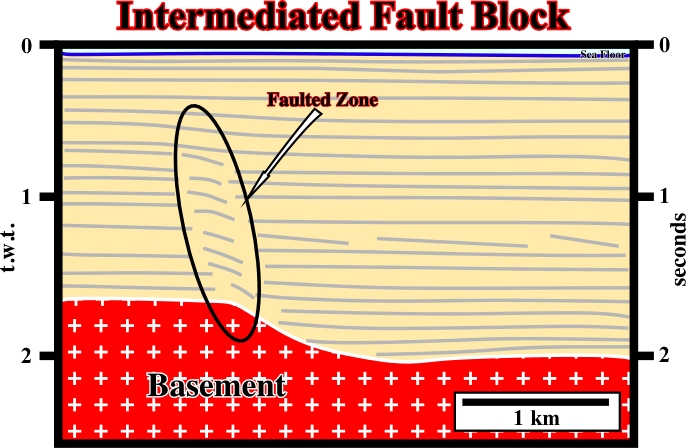
Fault scrap is the cliffs that represent the edge of a vertically displaced block.
A rollover anticline is a syn depositional structure developed within the downthrown block hanging wall of large listric normal faults.
The downthrown side is the side which went relatively down and is represented by such an arrow or the letter d.
Growth faults have two blocks.
A normal fault is one in which the hanging wall block is downthrown.
The downthrown block slips downward and basinward relative to the upthrown block.
This is only true of a normal fault b.
We need to know two things to determine fault type.
The non moving land is called the footwall.
Faults can be generalized into four principal types based on the direction and angle of movement.
An upthrown block between two normal faults dipping away from each other is a horst.
A normal fault is a fault in which the hanging foot wall block has moved upward relative to the hanging foot wall block.
The upthrown block the footwall is landward of the fault plane and the downthrown block the hanging wall is basinward of the fault plane.
Which of the following answers is the most accurate analysis of this statement.
A downthrown block between two normal faults dipping towards each other is a graben.
A fault in which hanging wall has apparently gone up with respect to the footwall is termed as reverse fault.
Niger delta mississippi delta.
A type of fault in which the hanging wall moves down relative to the footwall and the fault surface dips steeply commonly from 50 o to 90 o groups of normal faults can produce horst and graben topography or a series of relatively high and low standing fault blocks as seen in areas where the crust is rifting or being pulled apart by plate tectonic activity.
Downthrown block is the lowermost block of a fault.
A reverse fault is a fault in which the hanging foot wall block has moved downward.
Most deformations occur within the hanging wall side.
Fault normal fault reverse fault.
It depends on which side of the fault is the footwall which varies depending on the fault type c.
With strike slip faults sometimes the opposite.
Hanging wall represents the upper wall of a fault.
Note that both refer to the hanging wall block.
What is normal fault.
A normal fault is a type of dip slip fault where one side of land moves downward while the other side stays still.
Which side is the hanging wall and which side is upthrown and which downthrown.